Pre-med, short for pre-medical, refers to an academic and extracurricular pathway that undergraduate students pursue to prepare for medical school. This track includes coursework in the sciences, such as biology, chemistry, and physics, alongside studies in mathematics and humanities. Beyond academics, pre-med students engage in clinical experiences, research projects, and community service to gain hands-on knowledge and demonstrate a commitment to healthcare. The pre-med journey is designed to equip students with the foundational skills and experiences necessary for success in medical school and a future career in medicine.
The Trinity School of Biomedical Sciences Premedical Program is designed to provide both undergraduates and post- baccalaureate students a path to completing the requirements necessary for entry into medical school. The program advances students’ knowledge of careers in the health sciences and helps to strengthen their application to medical school. The Premedical Program is designed to work with undergraduate students who need to complete the necessary credit hours and required courses for entry into Trinity School of Medicine, or to assist students who have already achieved an undergraduate degree at an accredited U.S. university by allowing them to take or retake required courses to demonstrate mastery of the material and strengthen their application to medical school.
Click here to see the complete list of courses and curriculum.
Click here to see the complete list of courses and curriculum.
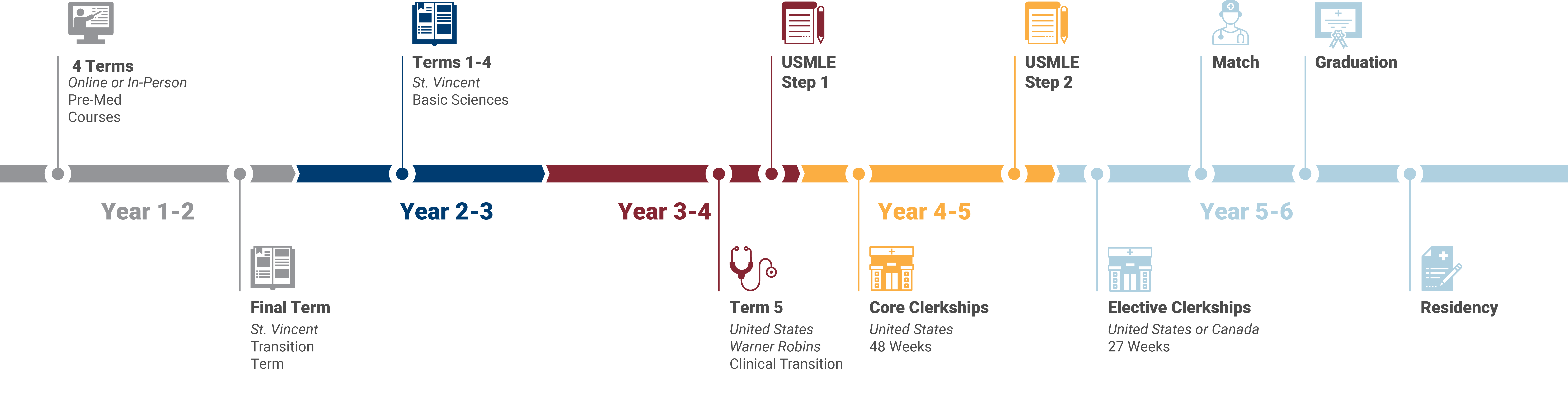
The pre-med timeline is a structured sequence of academic and extracurricular milestones designed to prepare students for medical school. It begins in the first year of undergraduate study with foundational courses in biology, chemistry, and mathematics. By the second year, students delve into more advanced science courses and begin participating in clinical experiences and research. The third year is dedicated to continuing clinical, and volunteer work, and starting the medical school application process. In the fourth year, students focus on completing their applications, attending interviews, and finalizing their undergraduate education. This timeline ensures that pre-med students build a competitive profile for medical school.
Apply to our pre-med program today and take the first step toward making a difference in healthcare.
Start your journey with us and turn your passion for medicine into a reality.
Welcome, prospective students, to a critical moment in your academic journey. As both the Provost of the University and the Dean of the Medical School, I welcome you to learn more about Trinity Medical Sciences University and Trinity School of Medicine. The landscape of medicine and medical education is evolving rapidly. Many of you come from diverse academic backgrounds, and some of you have been away from formal education for a while. This variety of experience enriches our learning community, bringing a wealth of perspectives to the field of medicine. However, it also means that your paths to medical school may vary significantly.
During the pandemic, educational institutions, including ours, tested different teaching modalities. One such method was asynchronous online education. While this offered flexibility, it lacked the real-time interaction and engagement found in synchronous learning or traditional in-person classes. Recognizing this, Trinity has strategically moved away from asynchronous online learning, especially in areas critical to medical education. This has significantly benefitted our current students.
The journey through our premed curriculum is designed to both impart knowledge and progressively immerse you in the culture and rigor of medical education. This curriculum aligns with the requirements set forth by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), ensuring that you are thoroughly prepared for the challenges ahead in medical school.
For some of you, only a few classes may be needed to bridge the gap to medical school. For others, the full spectrum of the premed curriculum will be instrumental in building a strong foundation. This curriculum is structured to build upon each previous semester, steadily integrating more complex concepts and fostering a deeper understanding of the foundation needed to thrive in medical school.
Our medical school curriculum culminates in the transitional semester, a pivotal phase designed specifically to prepare you for the first term at Trinity School of Medicine. This semester acts as a bridge, easing the transition from undergraduate studies to the rigors of medical school.
Lastly, I want to emphasize our commitment to your success. Students who diligently follow our premed curriculum and maintain a minimum GPA of 3.0 out of 4.0 are guaranteed admission to Trinity School of Medicine. This is a testament to our belief in the effectiveness of our educational approach and our dedication to nurturing the next generation of medical professionals.
Trinity invites you to embrace this journey with determination and an open mind. The road to becoming a medical professional is challenging, but it is also immensely rewarding. At Trinity, we are committed to supporting you every step of the way, ensuring that you not only succeed in medical school but also emerge as compassionate, skilled, and innovative leaders in healthcare. Welcome to a journey that will redefine your future and impact countless lives.
Investing in your future as a medical professional starts with understanding the costs associated with your education. Our pre-med program offers a competitive tuition structure designed to provide excellent value for a comprehensive preparatory education. Detailed information on tuition and fees, including payment plans and financial aid options, is available to help you manage and plan for your educational expenses.
Final term of PM and Terms l-X MD Program (estimated cost). Student health insurance includes evacuation to the U.S.
Basic Sciences
Trinity offers a range of apartments and residence halls for students. These options are available both on campus and in close proximity to campus (within 1/4 mile). The apartments come in various sizes, from one to four bedrooms. They are fully furnished and include amenities such as fully-equipped kitchens, high-speed internet access, and air conditioning. Both the residence halls and apartments have access to Trinity’s transportation services and provide 24-hour on-site security. Students are required to live in campus housing. This requirement ensures that students have easy access to their academic resources and support systems.
Click here for more information
Clinical Housing
Trinity has a new housing facility for students in Warner Robins. The complex is situated next to the Sonny Watson Health Science building, where clinical students engage in clinical skills labs and workshops. Each apartment comes fully furnished, and the monthly rate covers utilities, internet, elevator access, gated onsite parking, a fully equipped fitness center, and a resort-style saltwater pool. Additionally, Lofts at Houston Central will include around 5,000 square feet of retail space, with a focus on quick-serve eateries, unique sit-down restaurants, and complementary retail options. Students entering term 5 are required to live at the Lofts.
Food and entertainment are estimated to cost approximately $2000 to $2500 per term.
All monetary amounts mentioned on the site are in U.S.-denominated funds.
Trinity School of Medicine reserves the right to change tuition and adjust fees or to establish additional fees/charges whenever in their opinion such action is deemed necessary.
We understand the financial commitment of pursuing a career in medicine. Explore our scholarship and grant options to support your pre-med education. From merit-based scholarships to need-based grants, we’re dedicated to helping you achieve your goals. Explore our financial aid opportunities today.
As a leading pre-med Caribbean medical school, Trinity School of Medicine offers a well-rounded selection of common pre-med courses that lay a strong foundation for aspiring medical professionals. These courses encompass essential disciplines such as biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics, providing students with a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental sciences. Through a rigorous curriculum and expert faculty, Trinity ensures that students acquire the knowledge and critical thinking skills necessary to excel in their medical studies.
Undergraduate courses available include but are not limited to the following.
This course is designed to introduce students to the fundamentals of biology. A chemical and molecular approach is used to study the structure and function of living organisms. It also deals with the principles of evolution, diversity of life, and ecosystems. Emphasis is given to various organ systems that work together to perform coordinated functions while contributing a particular function to the body. 3 credits
This course provides the necessary framework to learn the basic rules and elements of medical terms. The course will focus on how to break down medical terms into their components: prefix, suffix and root. By learning the individual parts of medical terms, students will be able to understand their origins, definitions and abbreviations in addition to pronunciation and spelling. 3 credits
This course provides a combination of computer science, systems, and communications to address computer literacy needed to effectively collect, manipulate, collaborate and publish health science information. 3 credits
This course covers the growth and development through the lifespan—including physical, cognitive and socioemotional changes through each stage of life. Students come to better understand psychological theories and concepts as they learn about key topics in each of these stages, including genetics, attachment, education, learning, disabilities, parenting, family life, aging, generativity, moral development, illnesses, and attitudes towards death and dying. 3 credits
This course provides basic concepts of microbiology with emphasis on microbial pathogenesis and immunity. Topics include the chemical and physical nature of human microbial pathogens, aspects of medical microbiology, identification and control of pathogens, development and spread of antibiotic resistance, disease transmission and host resistance. The course also illustrates the general principles and techniques of infectious diseases. 3 credits
This course introduces the concepts of epidemiology and focuses on the great epidemics of the world. The timelines of epidemics will be explored along with the causative factors influencing the progression of the disease and factors leading to decline of disease. 3 credits
This course is designed to provide students with an understanding of the structure, function and regulation of the organ systems of the body and physiological integration of the systems to maintain homeostasis. Course content includes study of the musculoskeletal, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, urinary, immune, reproductive, and endocrine systems. The course covers the anatomical terminology to describe the basic structures of the human body. 3 credits
This course provides the basic concepts of the molecular architecture of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells and organelles, including membrane structure and dynamics. Included are how these components are used to generate and utilize energy in cells during cell motility, division, cell cycle, adaptation, injury, and cell death. 3 credits
This course introduces the foundational theories that guide modern psychology and provides students with a conceptual framework for understanding the day to day applications of these principles. The course content includes the biology of behavior, learning, memory, cognition, motivation, emotion, personality, abnormal behavior and its therapies, social behavior and individual differences. 3 credits
This course provides students with an understanding of the function and regulation of the organ systems of the body and physiological integration of the systems to maintain homeostasis. Students receive a quantitative and integrated concept of sub-cellular, cellular and organ systems. 3 credits
This course gives students the opportunity to explore the world of medical concepts from both contemporary and historical perspectives. Students are provided with an apprenticeship in concept clarification, concept evaluation, and argument. They are taught the specific skills to inquire, reason, and make judgments. The history of medical ethics, major views regarding medical issues such as the conflicts between different types of benefits to patients, physician duties, or patient autonomy are discussed. 3 credits
This course introduces the students to the basic concepts of inheritance, populations, mutations, and techniques used to assess each of these. 3 credits
This course introduces students to the two types of research, qualitative and quantitative, and their associated research methods. Students will be provided with the skills needed to select the appropriate research design, carry out the research and perform the data analysis where necessary. 3 credits
This course is designed to provide an overview of pharmacologic principles with an emphasis on therapeutic drug classification. For each therapeutic drug classification, basic mechanisms of drug actions, side effects, routes of administration, and common indications will be reviewed. Students will become familiar with common abbreviations and vocabulary terms related to drug therapy. The course will prepare students to recognize major drugs. 3 credits
This course provides new students with an orientation to the college environment. It works to build more capable lifelong learners by combining conceptual knowledge with practical strategies and skills. With engaging content and a focus on applying course concepts to real-world situations, College Success is particularly helpful for first generation students. 3 credits
This course provides students with the fundamental concepts of the chemical processes, enabling students to use chemical concepts in daily living and in the understanding of biochemistry. It covers matter, periodic table, writing and balancing chemical reactions, chemical composition and properties of compounds and modern atomic theory. It includes atomic structure, stoichiometry, understanding the symbols of elements and topics developed by thoughtful integration of problem-based instruction. This course further emphasizes the applications of chemistry in the field of medicine. Chemical reactions, equilibrium, acids and bases, conjugate acids and bases, thermodynamics, colligative properties of solutions, gas
laws, electrochemistry and topics related to biochemistry are included. This course enables the students to improve their problem-solving skills and mathematical skills. The course structure is designed to enhance the connections between theory and practice by engaging students. 3 credits
This course covers basic principles of structure and nomenclature of organic compounds, both aliphatic and aromatic. It emphasizes the principles of chemical reactions of organic compounds and the synthesis or degradation of bio-molecules in human metabolism. Saturated hydrocarbons, unsaturated hydrocarbons, synthesis, properties and reactions of alcohols, identification of functional groups, hybridization of hydrocarbons, stereochemistry cis-trans isomerism and addition reactions are covered. 3 credits
This course is a further study of the chemistry of carbon compounds from a functional group perspective. The course covers structure and nomenclature of specific organic compounds like thiols, aldehydes, ketones, amines, esters, carboxylic acids, carboxylic acids derivatives, benzene, phenol, Hofmann elimination reaction, Sn1, Sn2, E1 and E2 reactions. Emphasis is given on reactions, preparations, uses, and simple mechanisms and their biological application. 3 credits
This course provides students with a basic understanding of the biomolecules involved in the molecular architecture of eukaryotic cells and organelles. The course also describes the structural and functional properties of different biomolecules (carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids), the principles of bioenergetics, concepts of enzymology, and nutritional biochemistry. 3 credits
This course is designed for students needing to improve their proficiency in comprehension and expression of the English language used in the U.S. It provides an understanding of effective communication through writing and speaking methods. 3 credits
This course extends the skills of communication and critical thinking through additional analysis of reading and writing tasks to support skills development. 3 credits
Students learn the theoretical and practical skills they need to deliver effective, well researched oral presentations. The course covers essential communication skills including listening and feedback, audience analysis, research and information literacy, and ethics. It offers practical advice about making one’s voice heard (literally and figuratively), and introduces students to the major speech types, including informative, persuasive, and special occasion speeches. 3 credits
This course exposes students to the basic communication strategies such as speaking, listening, observing and memory training. 3 credits
This course builds on Communication Skills I and offers students practical experience in honing skills learned in Communication Skills I so as to develop interpersonal communication competency. 3 credits
This course provides the foundation for calculus. Trigonometry, exponential, logarithmic and polynomial functions are taught along with the concepts of limits and continuity. This course will include critical thinking and decision-making. 3 credits
Calculus deals with concepts of differentiation and integration and their applications. Students will learn to differentiate first principles and from the use of the Product, Quotient, and Chain Rules. They will also nudge up against the applications of maxima and minima. In integration, they will apply the definite integral, calculate areas and volume, do mathematical modeling, and solve differential equations. 3 credits
This course is an introduction to statistical concepts and analytical methods as applied to data in biomedical sciences. It emphasizes the basic concepts of quantitative analysis of data, and statistical inferences. Topics include: probability, frequency distributions, central tendency and dispersion; hypothesis testing, confidence intervals for means, variances and proportions; the chi-square statistics; data analysis and linear correlation. The course provides students a foundation to evaluate information critically. 3 credits
This course is a conceptual study of units and dimensions of physical quantities, vectors and kinematics, laws of motion and their applications, work and energy, properties of matter, sound, light and optics, gravitational motion, fluid mechanics and thermal physics. Students review the experimental methods associated with the basic laws of mechanics, vibration, circular motion, fluids, heat and thermal properties of materials. 3 credits
This course provides basic knowledge in biophysics. It enables the students to understand the concepts of human physiology. The course includes the study of electricity and magnetism, modern physics consisting of quantum physics, relativity, atomic physics, nuclear physics and nuclear medicine. The course is designed to increase problem-solving and analytical thinking skills. Students will complete research projects on the physics and applications of lasers, x-rays, ultra sounds and MRI. 3 credits
This course is designed to help students learn key concepts in cognition that will aid in their academic success. Course material introduces the concepts of reasoning, representation, cultural judgement, information literacy, and metacognitive reflection. Students learn through conscious development of key skills by active learning instead of the accumulation of knowledge by memorization. All learning is applied in the review of research and the formulation of skills to aid in discerning viable and reliable sources of information. 3 credits
This is the first in a two-course series to provide structure and support for students wishing to write a master’s thesis. This course will begin with the proposal of a research topic and methods and will conclude with the completion of the first four (4) sections of a thesis draft. This course will be followed immediately by RSCH 502 – Thesis Defense. 6 credits
This is the second in a two-course series to provide structure and support for students wishing to write a master’s thesis. In this course students will complete a final paper and defend it by presenting it to the faculty and dean. Prerequisite – RSCH 501. 6 credits
Don’t wait to pursue your dream of becoming a physician. Enroll in our pre-med program and equip yourself with the knowledge and experience needed for medical school.
Take the leap by applying today.
Whether you are unsure about meeting prerequisite requirements or seeking advice on strengthening your application, our admissions team is here to support you every step of the way. Fill out the form today and let’s kickstart your journey to medical school success.
A pre-med degree opens up a diverse array of career pathways within the healthcare industry and beyond. While the primary goal of a pre-med degree is to prepare students for medical school and a career as a physician, there are several other fulfilling options for graduates to explore, including:
Attending Trinity School of Medicine, a pre-med Caribbean medical school, presents a host of compelling advantages for prospective medical students. One of the key reasons to consider Trinity is its commitment to fostering a supportive and inclusive learning environment. The school prides itself on providing personalized attention and small class sizes, ensuring that students receive individualized instruction and ample opportunities for academic growth. Additionally, Trinity boasts a distinguished faculty comprised of experienced healthcare professionals who are dedicated to mentoring and guiding students throughout their medical journey.
Pre-health and pre-med are related but distinct paths in the journey towards a career in medicine or healthcare. While they share some common elements, they have different focuses and goals. Pre-health is a broader term that encompasses all undergraduate students who are interested in pursuing a career in healthcare, which includes fields beyond medicine such as dentistry, pharmacy, nursing, veterinary medicine, and more. Pre-health programs typically offer a diverse range of coursework and experiences to prepare students for various healthcare professions.
Students who successfully complete all requirements of their undergraduate program (90 credit hours) with a minimum 3.0 cumulative grade point average will be considered for promotion to Trinity School of Medicine’s Doctor of Medicine degree program.
Enrollment in Trinity School of Medicine’s 5-6 Year Pre-Med to Med Program will better prepare you for becoming a successful physician. Undergraduate students attend classes in a year-round format (trimesters), building towards promotion to the MD program in year two. The curriculum was designed with the same prerequisites U.S. students complete, giving students a level playing field for Step 1, Step 2 CK, and residency.
Other advantages include:
While English does not need to be your native language, applicants must be proficient in the English language or pass a TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language) exam. Students with non-English transcripts must have their credentials evaluated by World Education Services (WES), an accredited member of the National Association of Credential Evaluation Services.
Trinity Medical School is committed to upholding medical school accreditation standards. It undergoes regular evaluations and self-assessments to ensure compliance with the accrediting body’s requirements. The school continuously improves its curriculum, faculty qualifications, and educational resources to maintain the high standards set by the accrediting organization.
Office of Admissions & Administration
Basic Science Campus, St. Vincent